Bio e Natura
CHINESE PATHOGEN STUDY ON BLACK ROT
A study into the Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris responsible for major vegetable crop losses worldwide. Wheat, cocoa, melon and other could be badly affected
20 maggio 2005 | R. T.
Scientists at four major genomics and plant pathology laboratories in China have collaborated to find the causative agent of "black rot" disease, the most serious disease of vegetable crops worldwide.
Indeed for commercial growers, black rot is a significant issue. The fact that the pathogen can be seed-borne has led to seed certification programmes in developed countries, adding extensive cost and effort for suppliers and producers.
And if an outbreak does occur, then whole crops can be devastated.
This is because there is no effective treatment for Xcc infection. But now a team of scientists at four Chinese institutions - the Institute of Microbiology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Chinese National Human Genome Center at Shanghai, Guangxi University, and the Chinese National Human Genome Center at Beijing - have focused their efforts on characterising the genes responsible for Xcc pathogenicity with a view to finding a cure.
Black rot is caused by the pathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris (or Xcc). Under favourable conditions - high humidity and temperature - Xcc infects vegetable crops by spreading through the plants' vascular tissues, turning the veins in their leaves yellow and black, and causing V-shaped lesions along the margins of the leaves.
In their study, the team from China describe the identification of 75 different genes responsible for Xcc virulence. These genes appear to belong to 13 different functional categories or related metabolic pathways.
The researchers believe that the molecular characterisation of these pathogenicity-related genes will lead to the development of a treatment for "black rot" disease.
Employing whole-genome comparative genomic approaches, the scientists sequenced the complete genome of an Xcc strain that was isolated from an infected cauliflower plant in England during the 1950s. They then compared this sequence to a previously published sequence from a cabbage-derived Xcc strain.
Interestingly, they were able to identify three genes that were implicated in pathogenicity but that were not present in the previously described Xcc genomic sequence. To test the biological implications of this observation, they inoculated five different vegetable species with the three mutants corresponding to these strain-specific genes, and they observed significant differences in the response of each host species to infection.
These findings highlight the role of genome dynamics in the evolution of pathogenicity in Xcc in response to different host species.
The study, which represents the largest comparative and functional genomics screen for a plant or animal bacterial pathogen to date, is published online today in the journal Genome Research. Different forms of black rot can severely affect other aspects food production. Wheat for example is subject to more diseases than other grains, and, in some seasons, especially in wet ones, heavier losses can be sustained, pushing up prices for millers and bakers.
Cocoa production is another industry that can be badly affected, with some estimates putting losses as high as 30 per cent to 40 per cent of global cocoa production. These costs are often absorbed by processors and manufacturers under pressure to keep prices as low as possible.
Black rot can also devastate fruit crops. In 1997, an outbreak of black rot decimated the cantaloupe melon crop in the Rio Grande Valley of Texas, resulting in losses of $15 million.
Origin: Food Production Daily (www.foodproductiondaily.com)
Potrebbero interessarti
Bio e Natura
Miele al gusto di cacao con enormi benefici per la salute

Trasformati i sottoprodotti di cacao in un miele funzionale infuso di cioccolato ricco di antiossidanti e stimolanti naturali. Un prodotto che potrebbe trovare la sua via di mercato in alimenti gourmet e cosmetici
05 marzo 2026 | 15:30
Bio e Natura
Raggi gamma per migliorare sicurezza e conservazione del grano
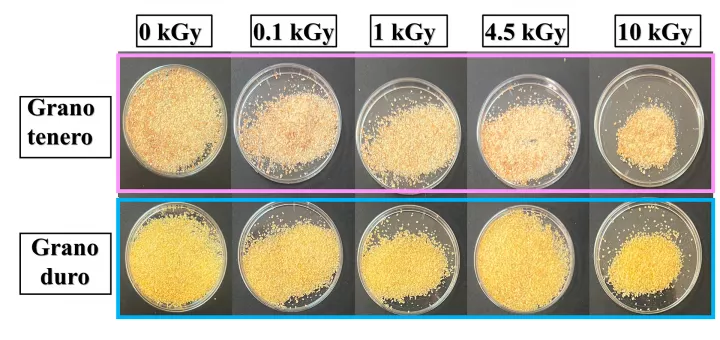
In Italia non è ancora molto diffusa la tecnica dell’irraggiamento gamma, usata solo per il trattamento anti-germinativo per patate, aglio e cipolla e per sanificare spezie e altri prodotti vegetali essiccati
28 febbraio 2026 | 12:00
Bio e Natura
Fitofarmaci nei suoli europei
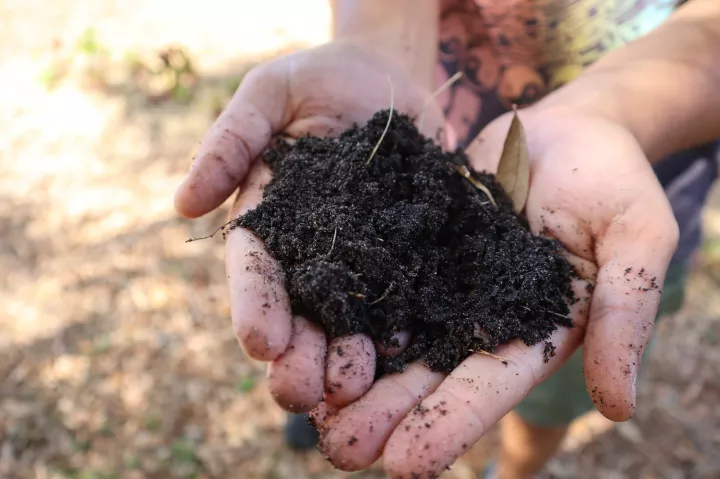

I ricercatori hanno analizzato campioni di terreno provenienti da diverse aree del continente: circa il 70% dei suoli esaminati contiene tracce di pesticidi. Tra i più colpiti ci sono i funghi micorrizici arbuscolari, microrganismi che vivono in simbiosi con le radici delle piante
23 febbraio 2026 | 15:00
Bio e Natura
Flower power: i fiori di melo da scarto a risorsa per l’industria
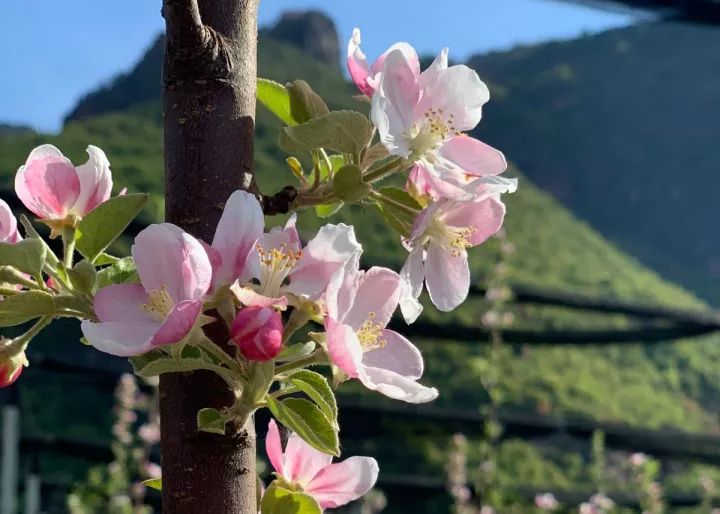

Uno studio del gruppo di ricerca di microbiologia degli alimenti Micro4Food della Libera Università di Bolzano ha dimostrato che la fermentazione dei fiori di melo permette di produrre estratti potenzialmente interessanti per l’industria alimentare, cosmetica e farmaceutica
01 febbraio 2026 | 11:00
Bio e Natura
Lo sviluppo delle filiere agroforestali e delle energie rinnovabili nei territori montani
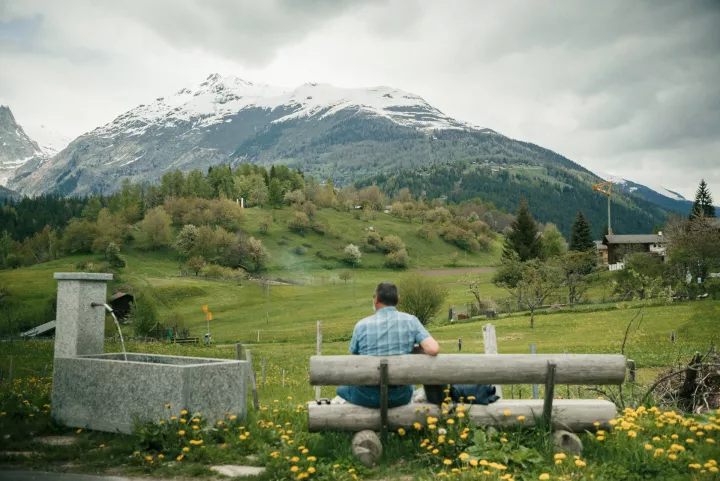

La programmazione comunitaria 2028-3034: il legno, la gestione, la pianificazione, la certificazione forestale, l’uso del legno per nuove energie, per impianti intelligenti domestici, comunali, per edifici pubblici e privati nel futuro
30 gennaio 2026 | 11:00 | Marcello Ortenzi
Bio e Natura
I microbi nascosti che decidono il sapore del lievito madre
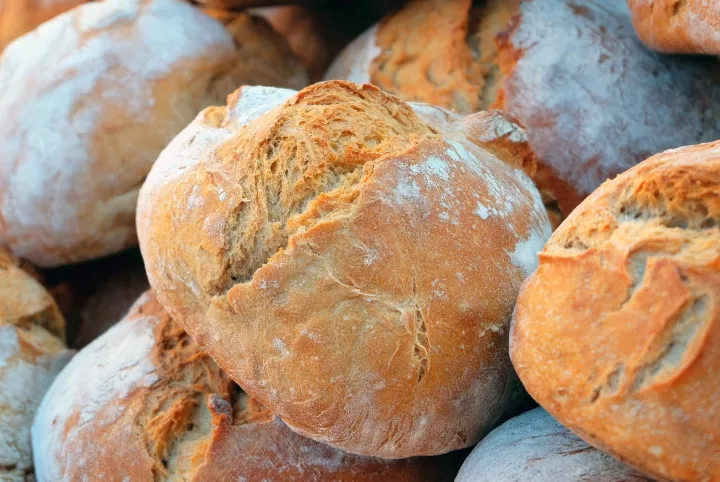

Farine diverse, come il grano integrale o la farina di pane, incoraggiano diverse comunità batteriche, che possono influenzare sottilmente il sapore, la consistenza e la fermentazione
29 gennaio 2026 | 14:00